ServiceNow Handler¶
The ServiceNow Handler enables seamless integration with ServiceNow as both a data source (read) and data sink (write) in SyGra workflows, using the PySNC library.
Features¶
- Read Operations: Query any ServiceNow table with filters, field selection, ordering, and pagination
- Write Operations: Insert new records, update existing records, or upsert (insert or update)
- Auto-Table Creation: Automatically creates custom tables (prefixed with
u_) if they don't exist - Multiple Auth Methods: Basic authentication, OAuth2 password grant flow, environment variables
- Flexible Querying: Dict-based filters or ServiceNow encoded query strings
- Batch Processing: Configurable batch sizes with automatic pagination
- Field Mapping: Automatic handling of custom table field prefixes (
u_)
Authentication¶
The handler supports three authentication methods (checked in order):
1. Environment Variables (Recommended)¶
export SNOW_INSTANCE="dev00000"
export SNOW_USERNAME="admin"
export SNOW_PASSWORD="your_password"
import os
import sygra
SNOW_INSTANCE = os.getenv("SNOW_INSTANCE")
source = sygra.data.from_servicenow(
instance=SNOW_INSTANCE,
table="incident",
limit=10
)
2. Basic Authentication¶
import sygra
source = sygra.data.from_servicenow(
instance="dev000000",
username="admin",
password="your_password",
table="incident"
)
3. OAuth2 Password Grant Flow¶
import sygra
source = sygra.data.from_servicenow(
instance="dev000000",
username="admin",
password="your_password",
oauth_client_id="your_client_id",
oauth_client_secret="your_client_secret",
table="incident"
)
Environment Variables for OAuth:
export SNOW_OAUTH_CLIENT_ID="your_client_id"
export SNOW_OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET="your_client_secret"
Source Configuration¶
YAML Configuration¶
data_config:
source:
type: servicenow
# Connection (optional if using environment variables)
instance: dev000000
username: admin
password: your_password
# Table Query
table: incident
# Filters (optional)
filters:
active: "true"
priority: ["1", "2"]
state:
operator: ">="
value: "2"
# OR use encoded query
query: "active=true^priorityIN1,2^stateNOTIN6,7"
# Field Selection
fields:
- sys_id
- number
- short_description
- description
- priority
- state
# Pagination & Ordering
limit: 100
batch_size: 100
order_by: sys_created_on
order_desc: true
# Advanced Options
display_value: "all"
exclude_reference_link: true
streaming: false
# Connection Options
proxy: null
verify_ssl: true
cert: null
auto_retry: true
Python Configuration¶
from sygra.core.dataset.servicenow_handler import ServiceNowHandler
from sygra.core.dataset.dataset_config import DataSourceConfig
config = DataSourceConfig(
type="servicenow",
instance="dev000000",
username="admin",
password="your_password",
table="incident",
filters={"active": "true", "priority": ["1", "2"]},
fields=["sys_id", "number", "short_description", "priority"],
limit=100,
batch_size=100,
order_by="sys_created_on",
order_desc=True
)
handler = ServiceNowHandler(source_config=config)
data = handler.read()
Sink Configuration¶
YAML Configuration¶
data_config:
sink:
type: servicenow
# Connection (optional if using environment variables)
instance: dev000000
username: admin
password: your_password
# Table & Operation
table: u_ai_incident_analysis # Target table (auto-created if starts with u_)
operation: insert # insert, update, or upsert (default: "insert")
key_field: sys_id # Field to match for update/upsert (default: "sys_id")
# Connection Options
proxy: null
verify_ssl: true
cert: null
auto_retry: true
Python Configuration¶
from sygra.core.dataset.dataset_config import OutputConfig
from sygra.core.dataset.servicenow_handler import ServiceNowHandler
output_config = OutputConfig(
type="servicenow",
instance="dev000000",
username="admin",
password="your_password",
table="u_ai_incident_analysis",
operation="insert",
key_field="sys_id"
)
handler = ServiceNowHandler(output_config=output_config)
handler.write(data)
Usage Examples¶
Example 1: Read and Export to File¶
import sygra
source = sygra.data.from_servicenow(
instance="dev000000",
table="incident",
filters={"active": "true", "priority": ["1", "2"]},
fields=["sys_id", "number", "short_description", "priority"],
limit=100
)
workflow = (
sygra.Workflow("export_incidents")
.source(source)
.sink("output/incidents.jsonl")
)
result = workflow.run()
Example 2: Read → AI Analysis → Write to Custom Table¶
import sygra
source = sygra.data.from_servicenow(
instance="dev000000",
table="incident",
filters={"active": "true", "priority": ["1", "2"]},
fields=["sys_id", "number", "short_description", "priority", "state"],
limit=10
)
sink = sygra.data.to_servicenow(
instance="dev000000",
table="u_ai_incident_analysis",
operation="insert"
)
workflow = (
sygra.Workflow("incident_analyzer")
.source(source)
.llm(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
prompt="""Analyze this ServiceNow incident:
Number: {number}
Description: {short_description}
Priority: {priority}
Provide JSON with:
- severity_score (1-10)
- predicted_resolution_time (hours)
- recommended_action (text)
- root_cause_category (technical/user/process/other)""",
output="ai_analysis"
)
.sink(sink)
)
result = workflow.run()
Example 3: Read → Update Existing Records¶
import sygra
source = sygra.data.from_servicenow(
instance="dev000000",
table="u_ai_incident_analysis",
fields=["sys_id", "u_short_description", "u_description"],
limit=5
)
sink = sygra.data.to_servicenow(
instance="dev000000",
table="u_ai_incident_analysis",
operation="update",
key_field="sys_id"
)
workflow = (
sygra.Workflow("paraphrase_updater")
.source(source)
.llm(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
temperature=0.7,
prompt="Create detailed paraphrase: {u_short_description}",
output="paraphrase"
)
.sink(sink)
)
result = workflow.run()
Example 4: ServiceNow to HuggingFace¶
import sygra
snow_source = sygra.data.from_servicenow(
instance="dev000000",
table="incident",
filters={"priority": ["1", "2", "3"]},
fields=["number", "short_description", "description", "priority"],
limit=1000
)
hf_sink = sygra.data.to_huggingface(
repo_id="your-org/servicenow-incidents",
private=True
)
workflow = (
sygra.Workflow("snow_to_hf_sync")
.source(snow_source)
.llm(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
prompt="Anonymize and clean: {short_description}",
output="cleaned_description"
)
.sink(hf_sink)
)
result = workflow.run()
Query Patterns¶
Simple Equality:
filters = {
"active": "true",
"priority": "1",
"state": "2"
}
Multiple Values (OR Logic):
filters = {
"priority": ["1", "2", "3"]
}
Complex Operators:
filters = {
"priority": {"operator": ">=", "value": "2"},
"sys_created_on": {"operator": ">", "value": "2024-01-01"}
}
Supported Operators: =, !=, >, >=, <, <=, IN, NOT IN, LIKE, STARTSWITH, ENDSWITH
Encoded Queries:
source = sygra.data.from_servicenow(
instance="dev000000",
table="incident",
query="active=true^priorityIN1,2,3^assigned_toISNOTEMPTY"
)
Write Operations¶
| Operation | Description | Requires key_field | Auto-creates tables |
|---|---|---|---|
| insert | Create new records | No | Yes (u_* tables) |
| update | Modify existing records | Yes | No |
| upsert | Insert or update based on key | Yes | Yes (u_* tables) |
Insert (with Auto-Table Creation):
sink = sygra.data.to_servicenow(
instance="dev000000",
table="u_ai_analysis",
operation="insert"
)
Update:
sink = sygra.data.to_servicenow(
instance="dev000000",
table="incident",
operation="update",
key_field="sys_id"
)
Upsert:
sink = sygra.data.to_servicenow(
instance="dev000000",
table="u_ai_analysis",
operation="upsert",
key_field="incident_number"
)
Working with multiple dataset¶
SyGra allow data generation engineer to connect multiple dataset, merge them into single and write into multiple dataset. This usecase can be very useful when working with multiple tables in ServiceNow instance.
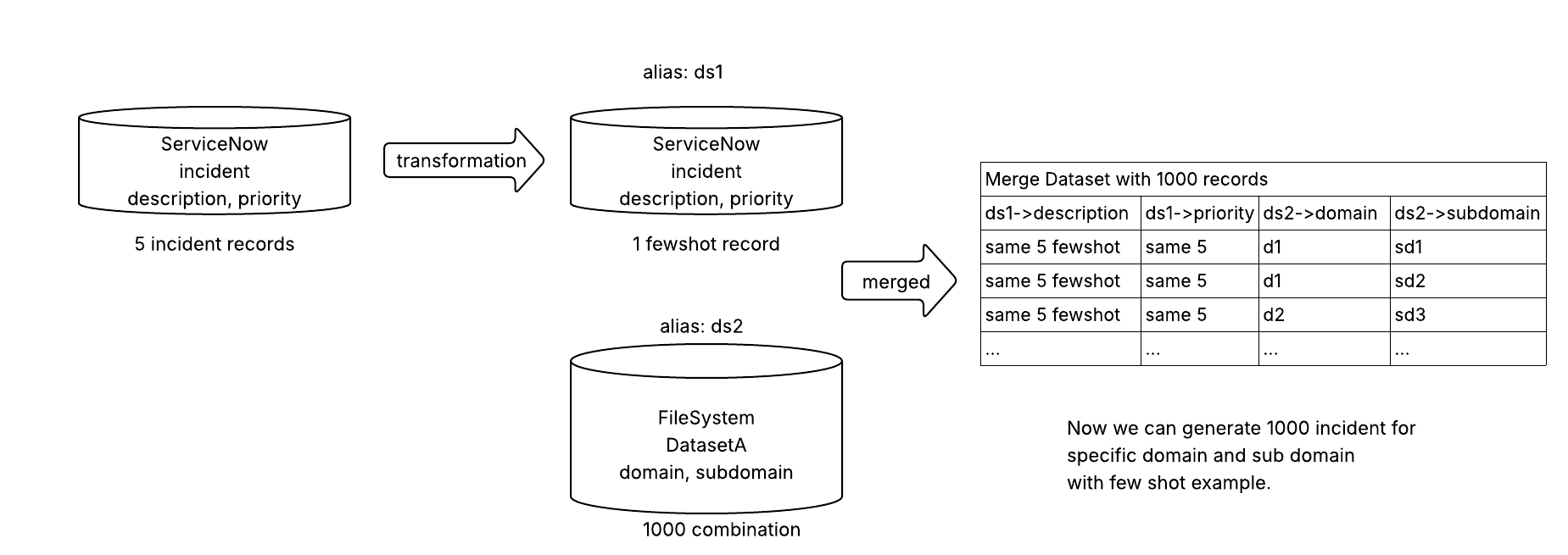
Let's look at the below scenario. We have ServiceNow instance with incident table contains 5 records, we want to generate many unique incident records with variety of domains.
First we will configure two datasets: one to fetch incident records and apply transform(CombineRecords) to create single record with 5 fewshot example, lets call it ds1(alias name).
Second, load domain and sub domain from a file(csv or json), lets call it ds2(alias name). Assume we have 100000 records, but we picked only 1000 records. We join the incident table(1 record) with file data as more columns.
Here we can use a 'cross' type join, which multiplies 2 dataset and creates final dataset.
The result dataset will contain columns or keys with prefix of alias name of the dataset, so column description will become ds1->description and domain will become ds2->domain.
In the graph yaml file, we can use the variables along with alias prefix like {ds2->domain}.
We also need to define multiple sink with alias name, in our case we only need one sink with alias name as ds1 as we are generating only incident records(ds1), however we can have multiple sink configuration to write data into various dataset.
Here is one example task with multiple dataset: tasks/examples/multiple_dataset
Extra parameters supported for dataset configuration as a list:
* alias: This variable gives a name to the dataset, so keys can be accessed in the prompt with alias prefix. The format to access in prompt alias_name->column
* join_type: Supports various join type like primary, cross, sequential, random, column.
* Horizontal or column based: In this join type, one dataset should have join_type: primary, where other dataset will be able to join in various ways:
* sequential: Dataset with this join type will sequentially pick one record and merge horizontally with one record from primary dataset. If the primary dataset is small, it will truncate and join, else it will rotate the record index.
* random: Dataset with this join type will pick one random record and merge horizontally with one record from primary dataset.
* cross: Dataset with this join type, will multiple with primary dataset. One record from this dataset will merge horizontally with each primary record. So, if this dataset has 10 records and primary has 100, final dataset will be 1000 records.
* column: This dataset type will use one column(join_key) and try to match with one column(primary_key) from primary dataset. This is same as RDBMS table join with foreign key.
* Vertical stack or row based: This type of joining is possible if there are matching column is the dataset. The join_key should be vstack for all the dataset in the list. A dataset transformation(rename column) can be applied to match the column name with other dataset.
During vstack merged dataset will have common column names, alias name will not be prefixed in the column name. Use variable name directly in the prompt, without the alias prefix.
Sink configuration should be a single configuration if aliasing not done in the python code.
primary_key: Signifies the column of the primary dataset which should match with other dataset columnjoin_keywhen join type iscolumnjoin_key: Signifies the column of other dataset which should match with primary dataset columnprimary_keywhen join type iscolumn
Example graph YAML for horizontal join¶
- Here each primary row is picked and merged(column wise) with one random row from secondary, generates 10 records only.
- If join_type of secondary is changed to
cross, each primary row is joined with each secondary row, generates 10 x n rows. - If join_type of secondary is changed to
sequential, each primary row is joined with one secondary row sequentially, generates 10 rows. - Example for join_type
columnis given attasks/examples/multiple_dataset# This graph config explains how incidents can be created for a role # as it is random horizontal join, the output record count is same as incident table(10) data_config: id_column: sys_id source: - alias: inc join_type: primary type: servicenow table: incident filters: active: "true" priority: ["1", "2"] fields: - sys_id - short_description - description limit: 10 order_by: sys_created_on order_desc: true - alias: roles join_type: random # join the secondary row randomly into primary type: "hf" repo_id: "fazni/roles-based-on-skills" config_name: "default" split: "test" sink: - alias: new_inc #type: "disk" file_path: "data/new_inc.json" file_type: "json" graph_config: nodes: incident_generator: node_type: llm model: name: gpt-5 temperature: 0.1 max_tokens: 1024 structured_output: schema: fields: description: type: str description: "Incident detailed description" short_description: type: str description: "Short summary of the incident in one line" input_key: input output_keys: - description - short_description # below post processor will just parse the string and return dict with description and short_description key post_process: tasks.examples.multiple_dataset_1.task_executor.AnalyzerPostProcessor prompt: - system: | You are an expert IT incident analyst. Analyze ServiceNow incidents and provide structured insights. - user: | Analyze this ServiceNow incident and create similar incident for the role {roles->Role}: - Short Description: {inc->short_description} - Full Description: {inc->description} edges: - from: START to: incident_generator - from: incident_generator to: END # this is added to rename the state variables into output format with aliasing (ex: new_inc->column_name) # column name should be the output column in the sink output_config: output_map: new_inc->description: from: "description" # generated description new_inc->short_description: from: "short_description" # generated short description new_inc->id: from: "inc->sys_id" # sys id from incident table new_inc->role: from: "roles->Role" # role from huggingface dataset
Advanced Features¶
1. Custom Table Field Prefixing¶
data = {
"incident_number": "INC0001",
"severity_score": 8
}
# Becomes in ServiceNow
{
"u_incident_number": "INC0001",
"u_severity_score": 8
}
2. Field Value Format¶
ServiceNow fields have both value and display_value.
3. Batch Processing¶
source = sygra.data.from_servicenow(
instance="dev000000",
table="incident",
limit=10000,
batch_size=500
)
4. Streaming Mode¶
source = sygra.data.from_servicenow(
instance="dev000000",
table="incident",
streaming=True,
batch_size=100
)
5. Connection Options¶
source = sygra.data.from_servicenow(
instance="dev000000",
table="incident",
proxy="http://proxy.company.com:8080",
verify_ssl=True,
cert="/path/to/client/cert.pem",
auto_retry=True
)
References¶
- PySNC Documentation: https://servicenow.github.io/PySNC/